● The Alliance has been set by five Horizon 2020 projects: EMB3Rs, INCUBIS, R-ACES, SO WHAT and S PARCS, which together have received a total of €14.5 million in funding from the European Commission.
● The main goal of the alliance is to maximise the projects’ impact and improve the quality and relevance of their outputs, ultimately contributing to boost energy efficiency, waste heat recovery, and energy cooperation in the European industries.
Brussels, Belgium, 13 April 2021; Five European projects working on waste heat recovery and industrial energy cooperation have joined forces and created an Alliance for Energy Cooperation in European Industries, setting up a common collaboration agreement that seeks to maximise their impact and improve the quality and the relevance of their outputs.
The establishment of the cooperation was completed on 7 March, with the approval of the “Letter of Intent of Energy Cooperation in European Industries”, during an online meeting. The five initiatives forming it, EMB3Rs, INCUBIS, R-ACES, SoWHat and S-PARCS, are funded under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme, and together they combine the efforts of 64 unique partners across 18 European countries, which have received a total of €14.5 Million in funding. The collaboration began back in November 2020, with a joint online workshop on waste heat recovery and energy cooperation in European industries. Further joint activities will include the cross-validation of public project outputs and joint communication, dissemination, and training actions.
The next public upcoming action is the participation in a joint workshop that the S-PARCS partners are organising as part of this project’s final event. The five initiatives will work together in a co-creation session to define the main barriers they have identified in the valorisation of excess heat/cold and energy symbiosis. After this workshop, the partners plan to invite stakeholders to contribute with further input, which will set the basis for a policy brief with guidelines on how to boost energy efficiency, waste heat recovery, and energy cooperation in the European industries.
EMB3Rs (User-driven Energy Matching & Business Prospection Tool for Industrial Excess Heat / Cold Reduction, Recovery and Redistribution; Grant Agreement N° 847121) is investigating the potential of recovering industrial excess heat and cold and designing a platform that explores how energy normally wasted by releasing it into the environment could be reused as a valuable source for other industrial processes, district heating, and cooling or further purposes.
INCUBIS (An Energy Symbiosis Incubator for Maximizing Energy Efficiency in Industrial Parks and Districts; Grant Agreement Nº 894800) will develop a set of tools and support services to help key stakeholders in Industrial Parks and Districts in the development and implementation of Energy Symbiosis projects. Energy Symbiosis involves the use of the excess heat/cold produced by one or more industries, to provide heating, cooling, or electricity for other industries or buildings. INCUBIS will deliver its tools and services through the Virtual Incubator model, supporting and building capacity in key organizations that are ideally
positioned to facilitate Energy Symbiosis projects and drive the project development process.
R-ACES (fRamework for Actual Cooperation on Energy on Sites and Parks; Grant Agreement Nº 892429) is supporting industrial clusters and business parks in becoming ecoregions that reduce their CO2 emissions by at least 10%. To achieve this, ecoregions are created where multiple stakeholders engage in energy cooperation by exchanging heat/cold streams, investing together in renewable energy solutions, or managing energy streams through smart energy management platforms. R-ACES is further drawing on and combining the knowledge and experience gathered throughout H2020 into a set of three specific
tools embedded in selected support actions: an assessment tool, legal decision support for joint contracts, and the smart energy management platform for clusters.
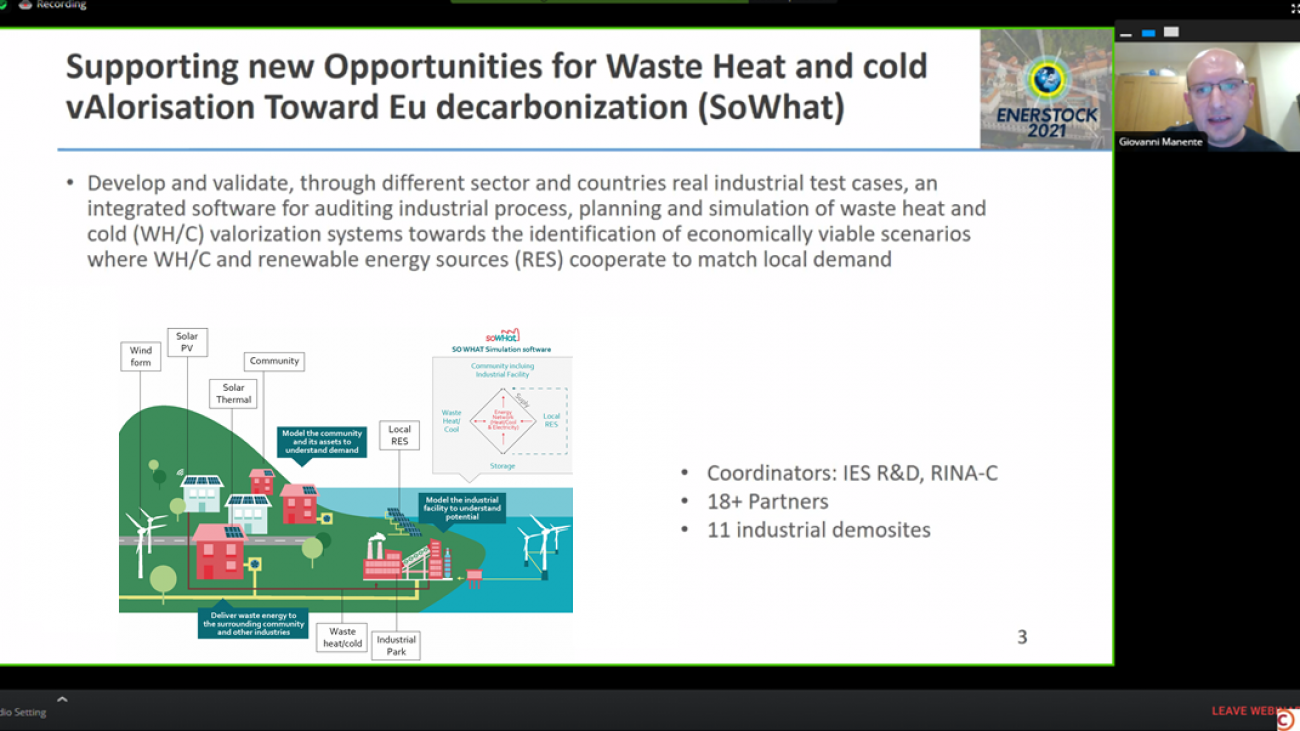
SoWHat (Supporting new Opportunities for Waste Heat And cold valorisation Towards EU Decarbonization; Grant Agreement Nº 847097) is developing an integrated software to identify and simulate how industrial WH/C could cost-effectively balance with the local community’s forecasted energy demand, and how this could be integrated with renewable energy systems. The tool, designed to support different stakeholders in auditing and mapping their energy processes, will assess the impact of energy processes on both a technical and non-technical level and help to reduce the cost of energy audits. This will be validated by 11 demonstration sites that will test the software in real operating conditions in industrial facilities.
S-PARCS (Envisioning and Testing New Models of Sustainable Energy Cooperation and Services in Industrial Parks; Grant Agreement Nº 785134) presents a sound concept for reducing energy costs and energy consumption in industrial parks, while, at the same time, increasing renewable on-site energy production. It aims at moving from a single-company energy-efficient intervention approach to cooperative energy-efficient solutions, enabling higher energy savings and the subsequent increase of competitiveness of the companies located in the parks. S-PARCS will systematically analyse technical, economic, regulatory, legal, organisational, environmental, and social barriers to energy-efficient park design and operation on all levels and will provide innovative, market-ready solutions to overcome them.
DOWNLOAD THE PRESS RELEASE